Discover 6 powerful pranayama breathing techniques backed by scientific research that support body development, mental clarity, stress reduction, and overall mind–body balance.

January 6, 2026 by N Bhowmik
6 powerful pranayama (yogic breathing) techniques
🌬️ What Is Pranayama? Meaning, Importance, and Health Value
Pranayama is the science of controlled breathing and a core component of traditional yoga practice. The word Pranayama comes from two Sanskrit terms: “Prana” meaning life energy or vital force, and “Ayama” meaning expansion or regulation. Together, pranayama refers to the conscious control and expansion of breath to influence physical, mental, and emotional health.
In modern wellness science, pranayama is recognized as a powerful mind-body technique that directly affects the nervous system, heart rate, lung function, and brain activity. Unlike physical exercise, pranayama works internally—calming the mind, balancing emotions, and improving oxygen delivery to every cell of the body.
Scientific research shows that regular pranayama practice can:
Reduce stress and anxiety
Improve lung capacity and respiratory health
Enhance focus and memory
Support heart health
Promote emotional stability
Below are six essential pranayama techniques, each explained with:
Definition
Step-by-step process
Benefits
Scientific evidence
Avoid / Awareness (precautions)
🌬️ 1. Deep Breathing (Dirga Pranayama)
Definition
Deep Breathing, also known as Dirga Pranayama, involves slow, full inhalation and exhalation using the diaphragm, chest, and upper lungs. It trains the body to breathe efficiently and calmly.
Process (How to Do It)
Sit comfortably or lie on your back
Inhale slowly through the nose, filling the belly first
Expand the chest and ribs
Exhale gently through the nose
Continue for 5–10 minutes
Benefits
Improves oxygen supply to the body
Reduces stress and anxiety
Enhances lung capacity
Calms the nervous system
Improves focus and mental clarity
Scientific Evidence
Studies in respiratory and mental health research show that deep breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, lowering cortisol levels and improving emotional regulation.
Avoid / Awareness
Do not force the breath
Avoid rapid breathing if dizzy
Practice slowly under guidance if new
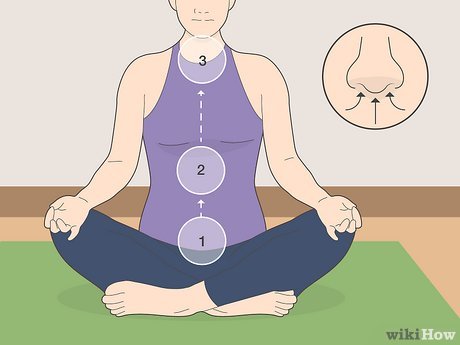
🌬️ 2. Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana)
Definition
Nadi Shodhana is a balancing pranayama that involves breathing alternately through each nostril to purify energy channels and calm the mind.
Process
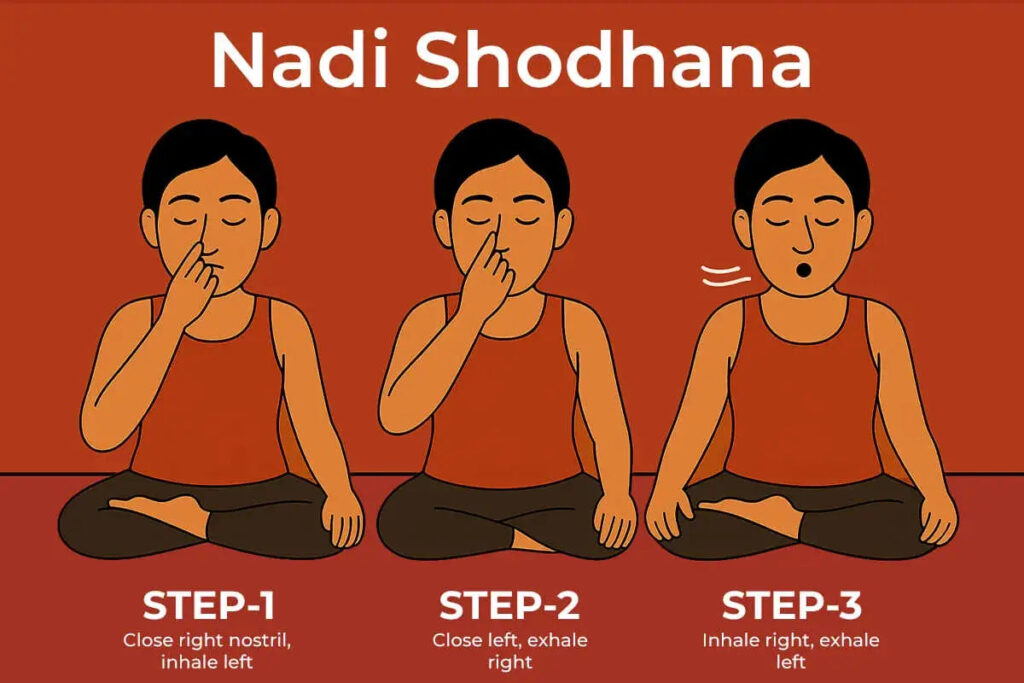
Sit upright with relaxed shoulders
Close the right nostril and inhale through the left
Close the left nostril and exhale through the right
Inhale through the right, exhale through the left
Continue for 5–7 minutes
Benefits
Balances left and right brain hemispheres
Reduces anxiety and emotional tension
Improves concentration
Supports heart health
Enhances mental calm
Scientific Evidence
Neuroscience-based studies show alternate nostril breathing improves autonomic balance and reduces stress-related nervous system activity.
Avoid / Awareness
Avoid during severe cold or nasal congestion
Do not rush the breathing cycle
Keep breathing gentle and natural
🌬️ 3. Belly Breathing (Diaphragmatic Breathing)
Definition
Belly breathing focuses on engaging the diaphragm fully, allowing the abdomen to expand and contract with each breath.
Process
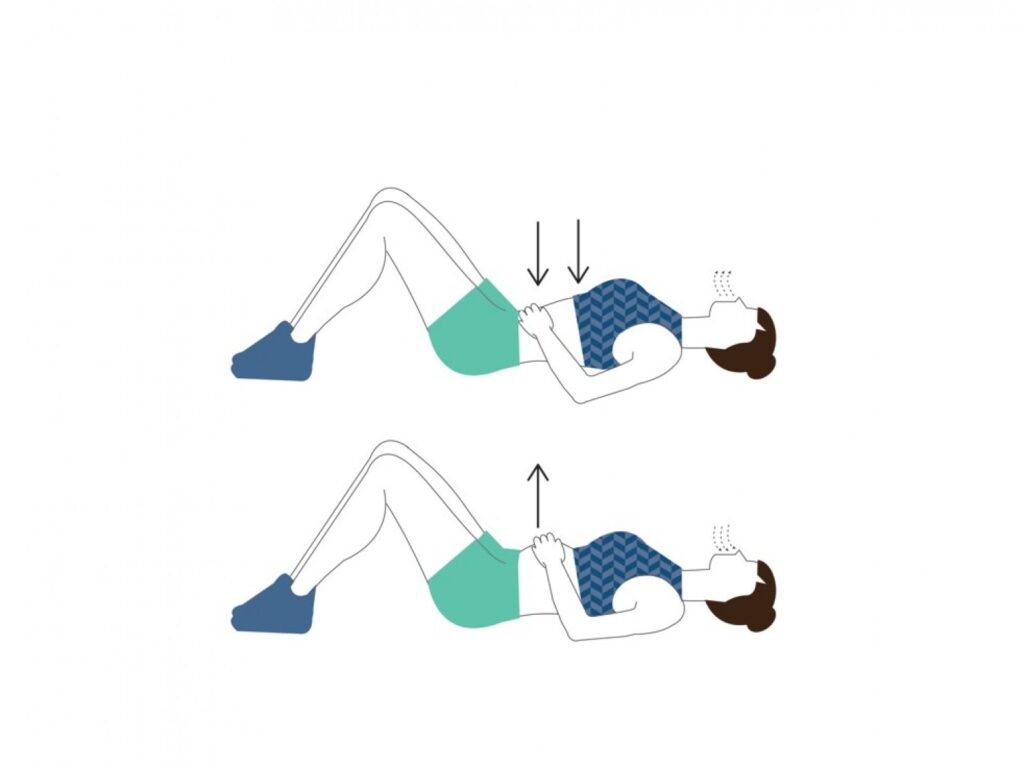
Place one hand on the chest, one on the belly
Inhale deeply so the belly rises
Exhale slowly, letting the belly fall
Continue for 5–10 minutes
Benefits
Improves digestion
Reduces blood pressure
Enhances lung efficiency
Promotes deep relaxation
Improves emotional balance
Scientific Evidence
Clinical research confirms diaphragmatic breathing improves heart-rate variability and reduces symptoms of stress-related disorders.
Avoid / Awareness
Avoid shallow chest breathing
Do not practice aggressively
Stop if discomfort occurs
🌬️ 4. Bhramari Pranayama (Humming Bee Breath)
Definition
Bhramari Pranayama involves making a gentle humming sound during exhalation, creating soothing vibrations in the head and nervous system.
Process

Sit comfortably and close your eyes
Inhale deeply through the nose
Exhale slowly while making a humming sound
Repeat 5–7 times
Benefits
Reduces anxiety and anger
Improves sleep quality
Calms racing thoughts
Enhances mental peace
Relieves mild headaches
Scientific Evidence
Psychological studies show humming vibrations stimulate the vagus nerve, helping regulate emotions and reduce stress.
Avoid / Awareness
Avoid if severe ear infection exists
Keep sound gentle, not loud
Practice in a quiet environment
🌬️ 5. Kapalbhati Pranayama (Skull-Shining Breath)
Definition
Kapalbhati is a cleansing breathing technique involving forceful exhalation and passive inhalation, primarily engaging the abdominal muscles.
Process
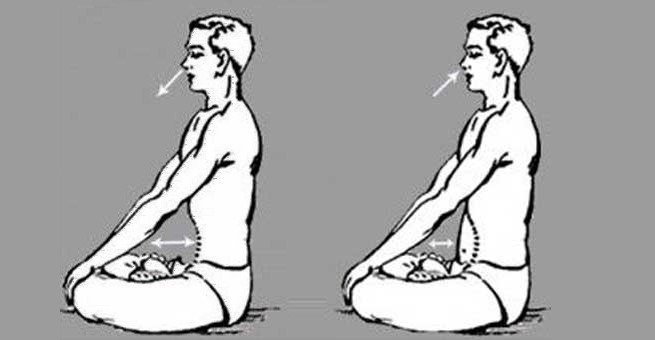
Sit with straight spine
Take a deep inhale
Exhale forcefully through the nose by contracting the abdomen
Inhalation happens naturally
Perform 20–30 rounds
Benefits
Improves digestion and metabolism
Strengthens abdominal muscles
Enhances lung function
Removes toxins
Increases energy levels
Scientific Evidence
Research indicates that controlled breath-based abdominal activation improves respiratory efficiency and metabolic function.
Avoid / Awareness
Avoid during pregnancy
Not recommended for heart problems
Practice only under expert supervision
🌬️ 6. Box Breathing (Equal Breathing)
Definition
Box Breathing involves inhaling, holding, exhaling, and holding the breath for equal counts, promoting mental focus and calmness.
Process

Inhale for 4 counts
Hold for 4 counts
Exhale for 4 counts
Hold again for 4 counts
Repeat for 5 minutes
Benefits
Enhances concentration
Reduces stress and panic
Improves emotional control
Supports mental resilience
Calms the nervous system
Scientific Evidence
Used by medical professionals and military training programs, box breathing is proven to improve stress tolerance and cognitive performance.
Avoid / Awareness
Do not over-hold the breath
Stop if dizziness occurs
Beginners should use shorter counts
🌬️ Conclusion
Pranayama is a powerful, science-backed practice that develops both body and mind from within. These six pranayama techniques improve breathing efficiency, calm the nervous system, sharpen mental focus, and promote emotional stability. When practiced regularly and correctly, pranayama becomes a lifelong tool for holistic well-being.
⚠️ Important Awareness Note
These breathing exercises should be practiced under the supervision of a qualified yoga or breathing expert, especially for individuals with medical conditions, respiratory issues, heart problems, or during pregnancy. This article is for informational purposes only.
Sources & References
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH)
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services – Yoga and breathing research
Harvard Health Publishing
Harvard Medical School – Breathing and stress regulation studies
PubMed
U.S. National Library of Medicine – Pranayama clinical research
National Institutes of Health (NIH) – PubMed Central (PMC)
Studies on breath control, nervous system, and mental health
Frontiers in Psychology (Peer-Reviewed Journal)
Research on breathing practices and emotional regulation
Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies
Evidence on pranayama, respiration, and mind-body integration
Yoga Journal (Educational Resource)
Pranayama techniques, safety, and alignment guidance